- IPv6
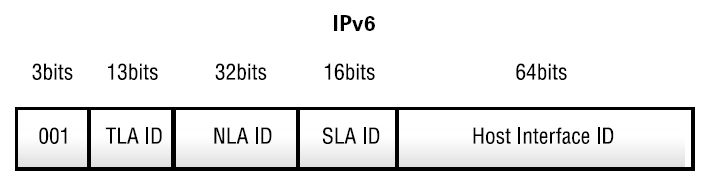
- The next version of the Internet Protocol, also called IP version 6 or IPng for IP next generation.The most striking feature of IPv6 is that it uses a 128-bit address space rather than the 32-bit system in use today. This provides for a truly astronomical number of possible addresses. The address format consists of 8 sections separated by colons. Each section contains 16 bits expressed as 4 hexadecimal numbers. An address might look like this: 1234:5678:9ABC:DEF0:1234:5678:9ABC :DEF0In any address, one set of leading zeros can be replaced by two colons.In addition to the 128-bit address space, IPv6 designates a 128-bit hierarchical address for point-to-point communication called an Aggregatable Global Unicast Address Format (AGUAF). In this format, a top level aggregator (TLA) is assigned a block of addresses by bodies such as the Internet Assigned Numbers Authority (IANA). In turn, the TLA assigns addresses to a next level aggregator (NLA), which in turn assigns addresses to the site level aggregator (SLA). In turn, the SLA assigns blocks of contiguous addresses to its subscribers. The last level is the host interface ID, which identifies a single host interface. Companies assign host interface IDs by using a unique number on the subnet.
 IPv6 assigns addresses to interfaces, and because a node can have multiple interfaces, it can also have multiple IP addresses. A single interface can also have multiple addresses. An address can be multicast, unicast, or anycast, which is a special case of multicast. The IP datagram header has been simplified, by dropping some fields and making others optional. IPv6 also allows for several types of optional header extensions, some of which might be used for specialized handling instructions. In addition, IPv6 includes the IPSec security extensions.
IPv6 assigns addresses to interfaces, and because a node can have multiple interfaces, it can also have multiple IP addresses. A single interface can also have multiple addresses. An address can be multicast, unicast, or anycast, which is a special case of multicast. The IP datagram header has been simplified, by dropping some fields and making others optional. IPv6 also allows for several types of optional header extensions, some of which might be used for specialized handling instructions. In addition, IPv6 includes the IPSec security extensions.
Dictionary of networking . 2014.
